RGGI Prices Rise as Emissions Continue to Fall
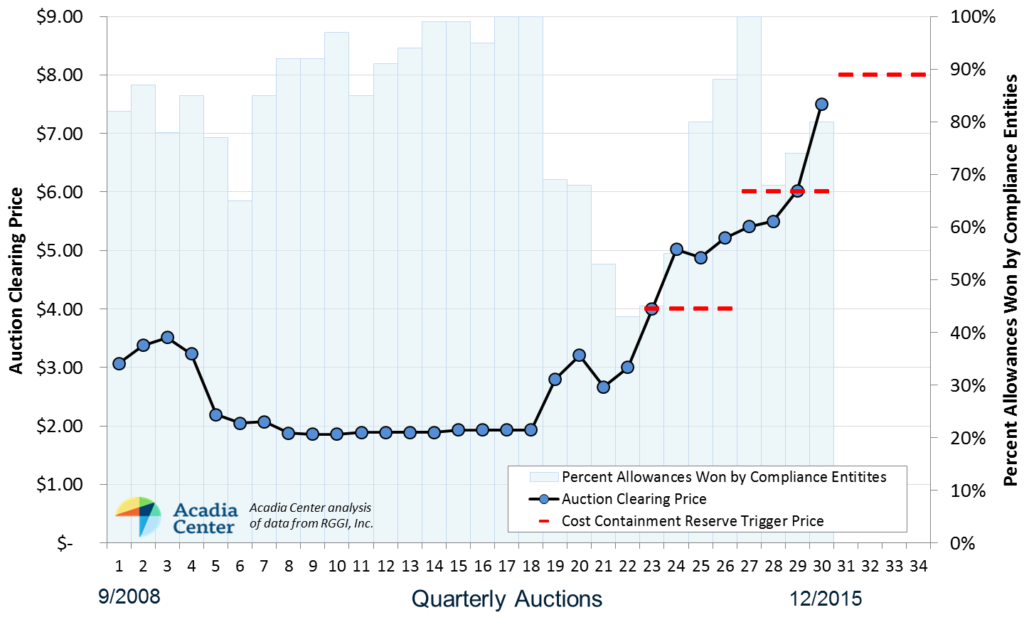
Results released today from RGGI’s 30th auction evidence the program’s continuing success, while also highlighting reforms needed to maximize environmental performance. All available allowances were sold at a clearing price of $7.50, 24% higher than the previous auction, and 44% higher than the clearing price from one year ago. The RGGI states raised $436 million dollars from the four auctions in 2015, and have now raised $2.37 billion for reinvestment since the program began, the majority of which has been used to fund energy efficiency and other consumer benefit programs. RGGI has been a successful model for reducing power sector emissions, and with reforms to ensure future environmental performance, it will be an effective means of complying with EPA’s Clean Power Plan.
The results of this latest auction show that the RGGI market continues to thrive while sending an increasingly significant price signal to the electric sector in favor of carbon-free resources. These rising prices serve as a vote of confidence in RGGI’s future as states begin a comprehensive review of the program. “The 2016 Program Review is a crucial opportunity for the RGGI states to continue to lead by example,” said Acadia Center President, Daniel Sosland. “The efforts of the RGGI states to review and improve the program have resulted in a model system for cost-effective carbon reduction that serves as a blueprint for states across the country.”
While today’s auction results demonstrate the RGGI model’s ability to drive real change in the energy sector, they also highlight one important change that will be necessary as part of this program review. The Cost Containment Reserve (CCR), which releases additional allowances when price triggers are met, will need to be reformed. As the graph below shows, price triggers have been exceed in both of the CCR’s first two years of operation, and the RGGI market appears poised to exceed the $8/ton price threshold in 2016.
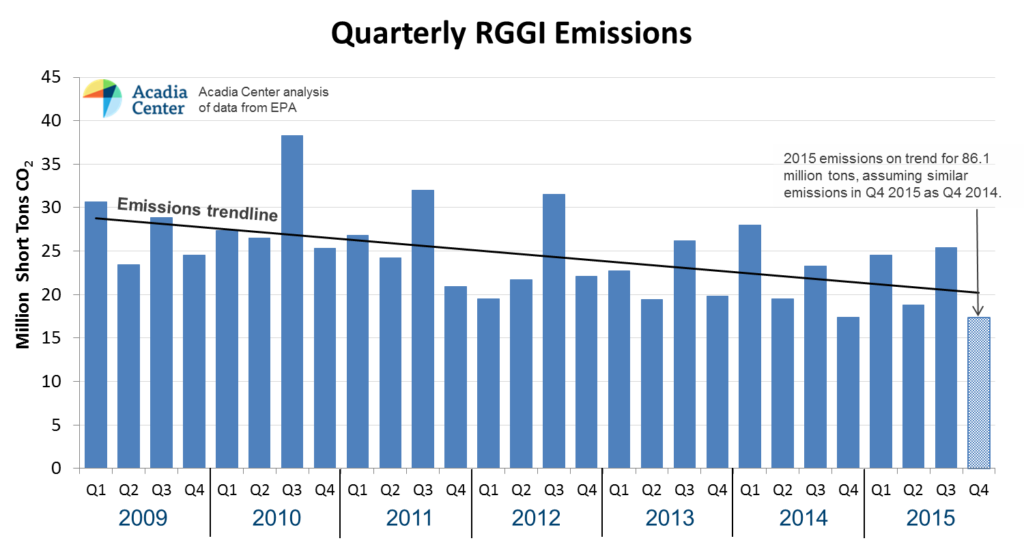
“The CCR is intended to mitigate price volatility by releasing an additional supply of allowances if increases in emissions create allowance shortages,” said Jordan Stutt, Policy Analyst with Acadia Center. “However, the CCR has been exhausted in both 2014 and 2015 even as emissions are trending downward, undermining progress towards emissions reductions in the power sector.” Emissions for 2015 are on trend to total 86 million tons, assuming fourth quarter emissions are similar to last year. Even with emissions below the cap in the last two years, 15 million additional allowances have been released by the CCR, and the current structure would allow for 65 million additional tons of CO2 emissions through 2020. To solve this problem, the CCR will have to either be eliminated, or restructured with higher trigger prices and allowances that are drawn from beneath the cap.
Stakeholders in the RGGI states will be submitting comments to RGGI, Inc. today to describe how the program could be strengthened, and how the RGGI states can continue their climate leadership under EPA’s Clean Power Plan. The comments will focus on the need to meet existing state climate goals, threshold considerations for expanding RGGI to other states, and technical fixes like reform of the CCR.
“As world leaders gather in Paris to discuss solutions to one of the planet’s greatest challenges, they can point to RGGI as a shining example of market-driven policy,” said Peter Shattuck, Director of Acadia Center’s Clean Energy Initiative. “The program’s success to-date has been proven; it’s now up to the RGGI states to signal their ambitions for the future.”
Additional information on RGGI’s performance to date, and role in EPA’s regulatory process are described in Acadia Center’s July, 2015 report: RGGI: A Model Program for the Power Sector
RGGI Overview:
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) is the first mandatory, market-based effort in the United States to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Nine Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states reduce CO2 emissions by setting an overall limit on emissions “allowances” which permit power plants to dispose of CO2 in the atmosphere. States sell allowances through auctions and invest proceeds in consumer benefit programs: energy efficiency, renewable energy, and other programs.
The official RGGI web site is: www.rggi.org
Contact:
Jordan Stutt, Policy Analyst
jstutt@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742-0054 x105
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
kdunlop@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742- 0054 x107
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.