Weatherization: The Little Climate Action that Could
New England is full of drafty houses. Regionally, almost a third of housing units were built before 1940, and more than half were built before the 1970’s, when the first building energy codes were adopted. Anyone who lives in such a house knows how uncomfortable it can be, on a February day, to feel the cold outside air seeping in through cracks around the windows and under the baseboard.
Less well-known is just how much these drafts contribute to the region’s greenhouse gas emissions. Acadia Center analysis shows that heating equipment in the draftiest houses can emit more than six times the CO2 of the same size house built to the current building code.
Not only is it possible to increase comfort and reduce energy bills in these drafty homes while also slashing emissions—it’s easy. Tens of thousands of New England homes undergo weatherization treatment through energy efficiency programs every year.
How does weatherization work?
Imagine poking holes in the bottom of a plastic cup and holding it under the tap. The larger the holes, the faster the water needs to come out of the tap to keep the cup full. Heating your home is like that: the cup is your house, the water is heat energy, the tap is your heating equipment, and the holes are—well, holes. Tiny cracks all around the house can let in cold air from the outside, while gaps in insulation allow heat to move faster through walls, ceilings, and floors. In the summer, heat and humidity can sneak in just as fast as they sneak out in the winter.
Weatherization is a way to slow the movement of heat by sealing up cracks and adding or improving insulation. Blocking the pathways that heat uses to escape your house means that heating and air conditioning equipment doesn’t need to work as hard, which saves money and avoids emissions.
Wait, I don’t see any cracks.
Like water, heat can move through spaces that are hard to spot. Window frames, door thresholds, fireplaces, switch plates, duct supply and return grilles, recessed light fixtures, attic hatches, and the joists that sit atop foundation walls are all common sites for air leakage. Homes settle over time, which unavoidably creates small cracks in all manner of locations.
Yikes! What can I do about that?
There’s an energy efficiency program in every Northeast state that will cover a big part of the cost of weatherization. These programs are designed to make it easier for homes and businesses to be more energy efficient, which benefits everyone. Weatherization work is often completely free for income-eligible households. Here is a list of programs by state:
| State | Residential | Income-Eligible |
| Connecticut | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
| Maine | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
| Massachusetts | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
| New Hampshire | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
| New York | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
| Rhode Island | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
| Vermont | Weatherization • All Rebates | Income-Based Offers |
Is there anything I can do myself?
Hiring a weatherization contractor will save you the most money, but some weatherization measures are easy enough for homeowners to do on their own. For example, V-seal weather stripping can be applied to the tracks of double-hung windows or sliding doors. Foam tubing on exterior door thresholds is also effective and easy to install. Caulking can be useful for larger gaps around baseboard molding and in the framing around windows and doors. Some caulking products dry clear, making the seal invisible. Others are white but can be painted.
Other types of air sealing projects are better completed by a professional. These include any work done on or near something hot—the vent for a furnace or clothes dryer, for example. Some projects are also just too onerous for building owners to do by themselves. While it may be technically possible to seal and insulate an entire attic as a DIY project, it is perhaps not advisable—for safety reasons, because of the effort involved, and because small mistakes can affect the success of the project.
Why would I insulate my attic?
While air sealing stops the movement of warm air through cracks, insulation stops the movement of heat through building components. Older homes very often have little or no insulation.
Heat moves slower through insulation because it’s full of air pockets—that’s why six inches of pink fiberglass insulates better than a brick wall four feet thick. Aside from fiberglass, contractors also commonly insulate with blown-in cellulose. Made from ground-up newspaper treated with a flame retardant, cellulose can often be inserted into wall cavities from the outside by temporarily removing a piece of siding, drilling a small hole, and then capping the hole when the insulating is complete.
Together, insulation and air sealing can improve the comfort of your home while cutting emissions. And because strong incentives are available no matter where in the Northeast you live, the work often pays itself off in bill savings in three years or less.
So this can save me money?
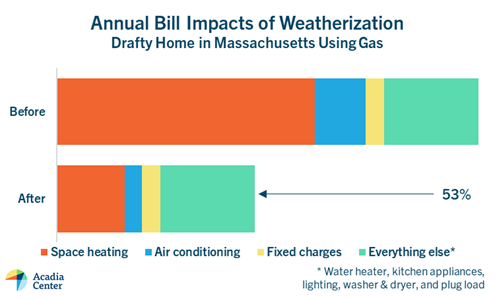
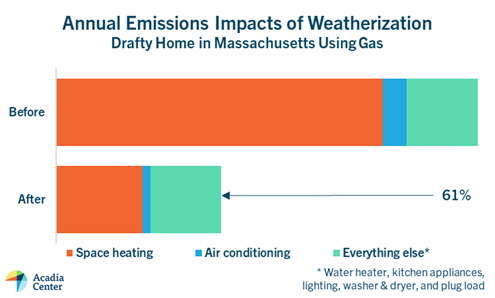
Weatherization is one of the best ways to save money on utility bills. For an older home, insulation and air sealing can reduce bills by more than 50% and emissions by 60% or more. If your heating bill in a cold winter month costs more than $250, look into weatherization.




















Follow us