RI Public Utilities Commission Votes to Eliminate Energy Waste in 2016
PROVIDENCE, RI – On December 16, 2015 the Rhode Island Public Utilities Commission unanimously approved the 2016 Energy Efficiency Plan for Rhode Island in order to help save consumers money on their utility bills and boost Rhode Island’s economy. This plan was developed collaboratively by key stakeholders representing a wide range of consumer interests, including the Division of Public Utilities and Carriers, the Office of Energy Resources, the Energy Efficiency and Resource Management Council, Acadia Center, People’s Power and Light, and Green and Healthy Homes.
In 2006, Rhode Island adopted the strategic and economic approach of investing in low cost energy efficiency in order to reduce consumers’ energy costs. In 2016, electricity from power plants like the Manchester Street Station in Providence will cost about 12 cents per kilowatt-hour, while the cost of eliminating wasted energy through efficiency improvements is about 5 cents per kilowatt-hour.
“Energy efficiency is an energy resource just like power from the coal and natural gas-fired power plants at Salem Harbor, Brayton Point, and Manchester Street. But energy efficiency is much cheaper, cleaner, and lower risk. In fact, the Public Utilities Commission’s decision to approve this plan is the best way to help customers save money,” said Acadia Center Rhode Island Director Abigail Anthony. Dr. Anthony represents environmental interests on the state’s Energy Efficiency and Resource Management Council (EERMC), which provides independent input and oversight to National Grid’s electric and natural gas efficiency programs.
Rhode Island’s energy efficiency programs help residents and businesses make energy efficient decisions by providing technical assistance and information coupled with financial incentives. For example, a residential electric or natural gas customer is eligible to receive a free home energy assessment during which the auditor will evaluate the lighting, insulation, appliance efficiency, and overall energy “fitness” of the home. The auditor will also inform the customer if she is eligible for financial incentives to help reduce the out-of-pocket cost of investing in energy efficient improvements, such as weatherization or new heating equipment. Loans are available to help homeowners and business owners with the up-front costs of efficiency upgrades.
These programs are proven and work for Rhode Island. The American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy has ranked Rhode Island in the top 5 states for energy efficient programs for the past 3 years. In addition to helping Rhode Islanders lower their utility bills, the state’s investments in low cost energy efficiency reduce the cost of doing business in the state, create jobs, and boost economic activity. The avoided spending on electricity and natural gas from the 2016 Energy Efficiency Plan will generate $265 million in economic benefits to Rhode Islanders and add $386 million to Gross State Product. Rhode Island’s energy efficiency programs directly support 639 jobs across 899 firms, more than 70 percent of which are located in Rhode Island.
In 2014, The Division of Public Utilities–the state agency charged with watching out for consumer interests– commissioned the research firm Synapse Energy Economics to see what efficiency is really doing for our electric bills. The analysis finds that a Rhode Island homeowner who gets a home energy assessment can save approximately 12% on her electric bill by replacing inefficient lighting and appliances and upgrading home insulation and weatherization. Factor in savings on natural gas or fuel oil use and total spending on energy is even lower. And small business customers, who are eligible for free energy audits, can save as much as 37% to 47% by installing high efficiency equipment and making recommended retrofits.
Contact:
Abigail Anthony, Rhode Island Director
401-474-8876, aanthony@acadiacenter.org
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
617-742-0054 x107, kdunlop@acadiacenter.org
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
RGGI Prices Rise as Emissions Continue to Fall
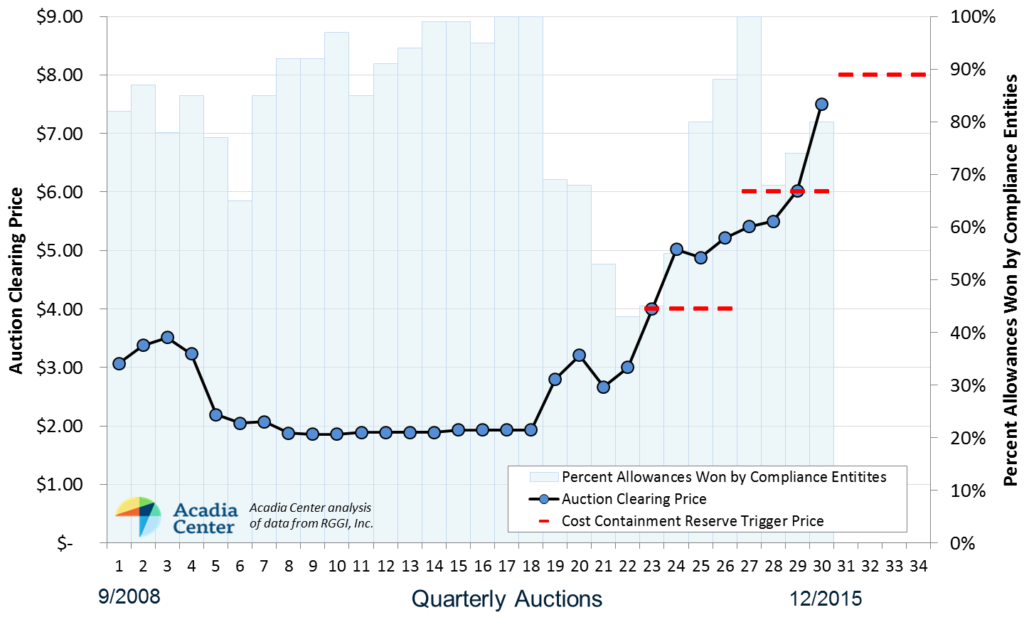
Results released today from RGGI’s 30th auction evidence the program’s continuing success, while also highlighting reforms needed to maximize environmental performance. All available allowances were sold at a clearing price of $7.50, 24% higher than the previous auction, and 44% higher than the clearing price from one year ago. The RGGI states raised $436 million dollars from the four auctions in 2015, and have now raised $2.37 billion for reinvestment since the program began, the majority of which has been used to fund energy efficiency and other consumer benefit programs. RGGI has been a successful model for reducing power sector emissions, and with reforms to ensure future environmental performance, it will be an effective means of complying with EPA’s Clean Power Plan.
The results of this latest auction show that the RGGI market continues to thrive while sending an increasingly significant price signal to the electric sector in favor of carbon-free resources. These rising prices serve as a vote of confidence in RGGI’s future as states begin a comprehensive review of the program. “The 2016 Program Review is a crucial opportunity for the RGGI states to continue to lead by example,” said Acadia Center President, Daniel Sosland. “The efforts of the RGGI states to review and improve the program have resulted in a model system for cost-effective carbon reduction that serves as a blueprint for states across the country.”
While today’s auction results demonstrate the RGGI model’s ability to drive real change in the energy sector, they also highlight one important change that will be necessary as part of this program review. The Cost Containment Reserve (CCR), which releases additional allowances when price triggers are met, will need to be reformed. As the graph below shows, price triggers have been exceed in both of the CCR’s first two years of operation, and the RGGI market appears poised to exceed the $8/ton price threshold in 2016.
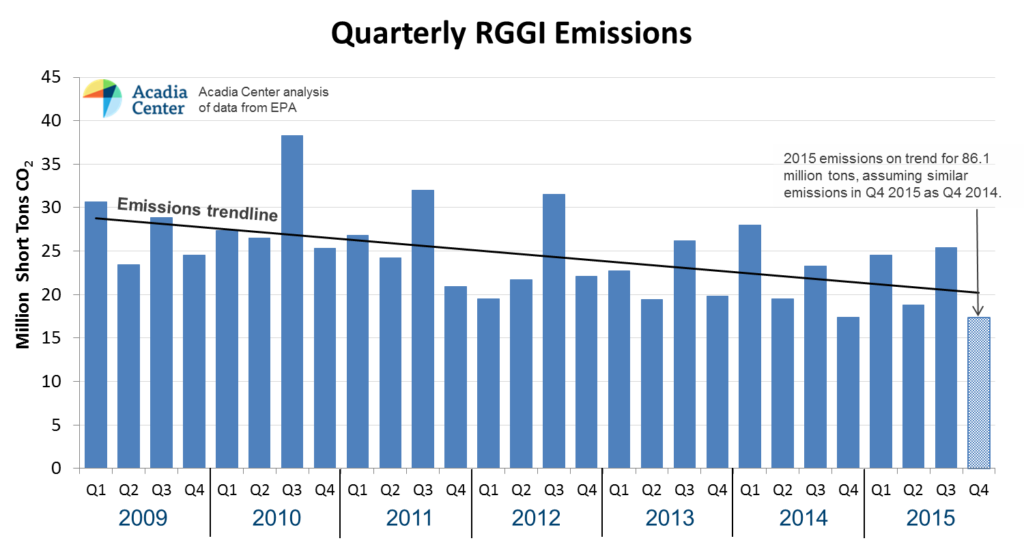
“The CCR is intended to mitigate price volatility by releasing an additional supply of allowances if increases in emissions create allowance shortages,” said Jordan Stutt, Policy Analyst with Acadia Center. “However, the CCR has been exhausted in both 2014 and 2015 even as emissions are trending downward, undermining progress towards emissions reductions in the power sector.” Emissions for 2015 are on trend to total 86 million tons, assuming fourth quarter emissions are similar to last year. Even with emissions below the cap in the last two years, 15 million additional allowances have been released by the CCR, and the current structure would allow for 65 million additional tons of CO2 emissions through 2020. To solve this problem, the CCR will have to either be eliminated, or restructured with higher trigger prices and allowances that are drawn from beneath the cap.
Stakeholders in the RGGI states will be submitting comments to RGGI, Inc. today to describe how the program could be strengthened, and how the RGGI states can continue their climate leadership under EPA’s Clean Power Plan. The comments will focus on the need to meet existing state climate goals, threshold considerations for expanding RGGI to other states, and technical fixes like reform of the CCR.
“As world leaders gather in Paris to discuss solutions to one of the planet’s greatest challenges, they can point to RGGI as a shining example of market-driven policy,” said Peter Shattuck, Director of Acadia Center’s Clean Energy Initiative. “The program’s success to-date has been proven; it’s now up to the RGGI states to signal their ambitions for the future.”
Additional information on RGGI’s performance to date, and role in EPA’s regulatory process are described in Acadia Center’s July, 2015 report: RGGI: A Model Program for the Power Sector
RGGI Overview:
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) is the first mandatory, market-based effort in the United States to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Nine Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states reduce CO2 emissions by setting an overall limit on emissions “allowances” which permit power plants to dispose of CO2 in the atmosphere. States sell allowances through auctions and invest proceeds in consumer benefit programs: energy efficiency, renewable energy, and other programs.
The official RGGI web site is: www.rggi.org
Contact:
Jordan Stutt, Policy Analyst
jstutt@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742-0054 x105
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
kdunlop@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742- 0054 x107
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
Massachusetts Would Set Highest Energy Savings Goals in the Nation with 2016-2018 Energy Efficiency Plan
Boston, MA– Massachusetts’ utilities have proposed the nation’s most ambitious energy efficiency programs, which will produce almost $8 billion in benefits over the next three years. The next chapter of the award-winning MassSave energy efficiency programs is now in the hands of the Department of Public Utilities, with a decision on the final proposed 2016-2018 Energy Efficiency Investment Plans expected by the end of January. Public comment on the plans is being heard today, November 30, 2015, beginning at 2 PM at the DPU’s offices at One South Station, 5th Floor.
The proposed plan features goals and strategies for saving energy and reducing bills for Massachusetts homes and businesses. If adopted, the programs will provide almost $8 billion in economic benefits and energy savings over the three year period – on top of $12.5 billion in benefits that the programs have delivered since 2008. The plan also sets the highest savings goals in the nation – annual reductions of 2.93% of electric retail sales and 1.24% of natural gas retail sales – even higher than the 2015 savings goals that resulted in Massachusetts being ranked #1 in energy efficiency by the American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy for the 5th year running. Energy savings would deliver environmental benefits equivalent to removing over 410,000 cars from the road.
“Massachusetts’ energy efficiency programs are delivering on their promise to create large energy savings for consumers, and move the Commonwealth toward a clean, affordable and secure energy future,” said Daniel L. Sosland, Acadia Center President. “Efficiency is the best near-term energy strategy for reducing Massachusetts’ residents’ energy bills. Investing in energy efficiency produces immediate bill savings that persist for years to come,” said Sosland.
The three-year plan was developed collaboratively with the state’s utilities and key stakeholders representing a wide range of consumer and environmental interests, including Acadia Center, the Energy Efficiency Advisory Council (EEAC), the Department of Energy Resources, and the Attorney General’s Office. By making successful use of the EEAC as a stakeholder council, the proposed plan improved markedly since the original draft in April. Among other factors, annual electric savings goals increased 17%, while the cost per unit of savings decreased 13%; and annual gas savings goals increased 15% while the cost per unit of savings decreased 6%, compared to the April 30th draft.
“Energy efficiency is a resource just like energy from Brayton Point, Pilgrim Nuclear, or other centralized power plants” said Acadia Center Senior Attorney, and EEAC representative, Amy Boyd. “But energy efficiency is much cheaper, cleaner, and lower risk. Approving this plan would be the best way to help customers save money.”
By investing in as much low-cost energy efficiency as possible, Massachusetts is reducing the cost of doing business in the state and leaving consumers with more money in their pockets. Such consumer savings are often spent right in Massachusetts —where they can support our local markets, our students, our education and health facilities—while payments to fossil fuel providers head immediately out of state. Every dollar invested in cost-effective energy efficiency boosts the Massachusetts Gross State Product an estimated $6.40 and every $1 million invested in energy efficiency generates around 43 job-years of employment.
Contact:
Amy Boyd, Senior Attorney
aboyd@acadiacenter.org , (617) 742-0054 x102
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
kdunlop@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742- 0054 x107
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
New Pipelines Unnecessary in New England: Facts Support Findings of MA Attorney General Study
BOSTON, MA – New publicly-funded natural gas pipelines in New England are unnecessary according to a new study by the Massachusetts Attorney General’s Office. This finding is validated by significant developments in the region’s energy markets, including:
- Improved planning and market reforms that have avoided electricity price increases despite record cold weather
- Expanded efficiency programs that are reducing energy demand cost-effectively
- Large-scale procurement for natural gas alternatives such as wind and hydroelectric power
- Backup generation that new natural gas power plants will install to reduce reliance on natural gas during infrequent peak demand periods
“Acadia Center has long argued that the public should not be forced into the novel role of underwriting expensive, risky, privately owned pipeline projects before a full and fair considerations of all viable alternatives,” said Daniel Sosland, President of Acadia Center. “The recommendations of this study prove the wisdom of not rushing to the conclusion that new pipelines are the only solution to a reliable and affordable energy system. It is encouraging to see that analysis is demonstrating that natural gas market reforms and clean energy alternatives offer better, more affordable options.”
Lower electric prices due to market reforms: Massachusetts’ electricity prices are declining due to improved planning and market reforms. Specifically, Eversource’s winter rate of 10.39 cents/kWh is 27% lower than last year’s rate, and National Grid’s rate of 13.03 cents/kWh is almost 25% lower than last year. Lower prices are due in part to market reforms implemented by the regional grid operator ISO-New England and planning requirements established by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. In conjunction these reforms are improving utilization of existing gas delivery infrastructure and leading power generators to develop plans for ensuring adequate fuel supplies during winter peak.
Energy efficiency reducing electricity demand: Massachusetts’ and other New England states’ aggressive energy efficiency programs are causing winter energy demand to decline, reducing the need for additional pipeline capacity and other energy infrastructure. Despite using conservative assumptions that overstate the cost and understate the impact of efficiency programs, ISO-NE predicts that winter peak demand will decline by 0.1% annually through 2024, and the actual impact of energy efficiency is likely far greater. Acadia Center has demonstrated that ISO-NE consistently overestimates energy consumption and peak demand: winter peak energy demand was 24% lower in 2014 than the 2006 projection, and total 2014 energy consumption was 17% lower than the 2006 projection. These inaccurate projections overstate the need for expensive energy infrastructure, including oversized natural gas pipelines that could be used to support gas exports overseas the majority of the year.
Clean energy procurement will displace gas generation: On November 12th Massachusetts, Connecticut and Rhode Island released a Request for Proposals (RFP) for significant quantities (up to 1,000MW plus) of hydroelectric, wind, and solar energy that will displace natural gas generation and reduce power sector natural gas demand. Legislative proposals in Massachusetts to procure additional hydroelectricity and wind could more than double the quantity of energy in the RFP, offsetting even more natural gas demand. It is worth noting that the costs for hydroelectricity and renewable energy are conservatively overstated in the Attorney General’s report, and actual prices for blended wind and hydroelectricity would have to be lower to compete in the regional electricity market.
Gas plants with limited backup generation: New power plants approved through the regional grid operator’s Forward Capacity Market Auction in early 2015 all include natural gas generation with oil backup. On the few coldest days when natural gas supplies are dedicated to meeting heating needs, these plants will run on oil. This modest, limited use of oil generation during winter peaks in the near term, before more renewable generation comes online, would have a far smaller impact on GHG emissions than new pipelines used year-round, and would be less expensive to consumers than pipeline expansion
“This study is matched by facts on the ground,” said Peter Shattuck, Massachusetts Director for Acadia Center who served on the report’s Study Advisory Group along with representatives from utilities, the natural gas industry, and clean energy and consumer groups. “Commonsense market reforms, improvements in energy efficiency, and new clean energy supplies coming online are already addressing winter price volatility, making it clear that massive outlays for subsidized gas pipelines are an unnecessary risk for Massachusetts citizens to bear.”
Peter Shattuck will be taking part in a press availability call at 11:30 EST today to discuss the findings of the report, joining leaders from the business, municipal, and health sectors, including:
- Jed Proujansky, Selectman of Northfield, Massachusetts.
- Andy Savitz, Director of Sustainability for the City of Newton and author of The Triple Bottom Line, a nationally-acclaimed handbook for business leaders seeking to embrace sustainable business practices.
- Tedd Saunders, Chief Sustainability Officer at the Saunders Hotel Group.
- Bill Ravanesi, Senior Energy Director with Health Care Without Harm.
CALL DETAILS:
Wednesday, November 18, 11:30 EST
Conference Call: 712-775-7031, PIN: 301-222-738.
Contact:
Peter Shattuck, Clean Energy Initiative Director
pshattuck@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742-0054 x103
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
kdunlop@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742- 0054 x107
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
Fair Competition Needed in Utility Energy Contracting
BOSTON, MA -Acadia Center joined with clean energy developers today in calling for fair consideration of alternatives to natural gas in meeting the region’s electricity needs. In a joint letter, Acadia Center and the other signatories request that utilities National Grid and Eversource redraft the solicitation to remove the current bias toward natural gas projects and ensure that a full array of cleaner, lower cost options are able to compete.
The letter is written in response to Requests for Proposals issued by the utilities on Friday October 23rd. The solicitation requires responses by November 13th – only a three week window – and seeks bids only from providers of liquefied natural gas, regional gas storage, and pipeline expansion projects. Eversource and National Grid are participants in at least one project that could qualify for contracts; the pipeline expansion and storage project Access Northeast.
The letter states: “In this RFP, the utilities limited their solicitation to a particular set of resources, gave notice to no other resources, and established a timeline so short, only their partners could submit timely responses. The RFP not only pre-judges the results by effectively barring competition, but also virtually guarantees that the Commonwealth’s ratepayers will pay more than necessary to achieve a reliable winter energy supply.”
The letter additionally notes that the proposed procurement does not appear to comply with Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities’ requirement that the proposed agreement compares favorably to “all energy resources reasonably available in the market that have the potential to address the objective of providing electricity at a reasonable cost and that compare favorably in terms of price and non-price factors.”
The procurement closes shortly before the expected release of a Regional Electrical Reliability Options Study undertaken by the Massachusetts Attorney General’s Office, and following the announcement of electricity rates for the winter of 2015-2016 that are lower than past years. Specifically, Eversource’s winter rate of 10.39 cents/kWh is 27% lower than last year, and National Grid’s rate of 13.03 cents/kWh is almost 25% lower than last year. In Rhode Island, National Grid’s proposed rate of 8.9 cents/kWh is over 20% lower than last winter’s basic service rates.
In an appendix to the letter, Acadia Center provides supporting information on the cost-effectiveness of energy efficiency as an alternative to natural gas supply. New England’s investments in energy efficiency have already proven valuable in winter: without the demand reductions achieved since 2000, ratepayers would have paid an additional $1.46B in winter 2014 alone. The appendix also describes how the region’s grid operator has consistently over-estimated future energy demand, potentially contributing to overbuilding of natural gas pipeline and other energy infrastructure. Specifically, Acadia Center demonstrates that ISO-NE has consistently overestimated energy consumption and peak demand, with actual energy demand coming in 17% lower in 2014 than the 2006 projection, and summer peak demand falling 20% in 2014 from 2006 predictions.
The letter and appendix can be found at: http://acadiacenter.org/document/joint-comments-on-massachusetts-utilities-gas-procurement/
Contact:
Peter Shattuck, Clean Energy Initiative Director
pshattuck@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742-0054 x103
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
kdunlop@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742- 0054 x107
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
Acadia Center Applauds Rhode Island’s Nation-Leading Efforts on Energy Efficiency
Rhode Island is tied with Massachusetts for first place in the utility-sector energy efficiency programs and policy category of the 2015 State Energy Efficiency Scorecard, released today by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE), a national nonpartisan organization. In terms of the overall ranking, Rhode Island is tied with Oregon for fourth place behind Massachusetts (#1), California (#2), and Vermont (#3). This is the third year that Rhode Island has ranked in the top five states.
Least Cost Procurement, first implemented 8 years ago and extended for another 5 years this summer, is largely responsible for Rhode Island’s continued leadership on energy efficiency. “Rhode Island continues to be a leader when it comes to energy efficiency,” said Daniel Sosland, Acadia Center’s President. “Investing in low-cost energy efficiency instead of expensive electricity and natural gas helps Rhode Islanders lower their energy bills and spurs economic growth,” said Sosland.
“Lower energy bills means more money is left at the end of the month to spend on other things, and most of that spending happens locally,” said Leslie Malone, Senior Analyst with Acadia Center. Since 2008, Rhode Island has invested over $558 million in energy efficiency and consumers have realized $1.99 billion in economic benefits. In its 2016 Energy Efficiency plan – recently filed with the Public Utilities Commission – National Grid proposes investing over $83 million in cost-effective efficiency programs to deliver electric savings that are 47% less expensive than the cost of supply, and natural gas savings that are 15% less than the cost of supply. The investments in 2016 will generate more than $256.1 million in direct benefits over the life of the efficiency measures, and add over $386.9 million to Rhode Island’s Gross State Product (GSP) and generate over 4,220 job-years of employment.
Acadia Center is a member of the Energy Efficiency Resource Management Council (EERMC), the stakeholder council charged with assisting with the development, implementation, and review of energy efficiency programs in Rhode Island. The EERMC is critical to the success of energy efficiency in the states, and Acadia Center looks forward to working with fellow members, utilities and other stakeholders to make sure that the plans are implemented effectively to deliver cost savings through lower utility bills, emissions reductions, and clean energy job growth, in addition to broader economic benefits.
See the Scorecard at: http://www.aceee.org/state-policy/scorecard
Contact:
Leslie Malone, Senior Analyst
401-276-0600, lmalone@acadiacenter.org
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
617-742-0054 x107, kdunlop@acadiacenter.org
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
Massachusetts Holds Off California to Receive Top Energy Efficiency Ranking for the Fifth Year in a Row
The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE), a national nonpartisan organization, released its 2015 State Energy Efficiency Scorecard today, with Massachusetts holding the #1 rank for the fifth year in a row, having overtaken California in 2011. California is still close behind at #2, with only a half point separating the states’ rankings.
Massachusetts has proven its continued commitment to energy efficiency under its Green Communities Act of 2008 by saving a large and growing percentage of energy every year through efficiency measures, and delivering over $11.5 billion in economic benefits and energy savings for ratepayers over the last five years.
Massachusetts’ next 3-year plan (2016-2018) is currently being evaluated by the Energy Efficiency Advisory Council, a stakeholder board on which Acadia Center serves. The draft plan is expected to deliver $8.13 billion in economic benefits and energy savings over the 3 year period, and sets savings goals (2.93% of sales for electric and 1.24% of sales for natural gas) that are believed to be the highest in the nation, yet again. The environmental benefits the 3-year plan will deliver are equivalent to removing an estimated 408,000 cars from the road.
“Maximizing efficiency is a major step toward securing a clean energy future. Massachusetts is showing that the principle of deploying least-cost, non-polluting measures to reduce demand really works. It’s a triple-win for the environment, the economy and the end users who enjoy lower costs and more effective energy use,” said Amy Boyd, Senior Attorney for Acadia Center, and member of the Energy Efficiency Advisory Council.
“The Northeast is on the right path, and leaps ahead of some other states, but there is still a lot to do to make the most of this low-cost, clean resource. The states can work to find better ways to treat older buildings, provide new financing tools and technologies, and accelerate strategies to reach untreated homes and businesses,” said Boyd.
As a member of efficiency stakeholder boards in multiple states, Acadia Center looks forward to working with fellow members, utilities and other stakeholders to make sure that the efficiency plans for Massachusetts and other New England states are implemented effectively to deliver cost savings through lower utility bills, emissions reductions, and clean energy job growth, in addition to broader economic benefits.
See the Scorecard at: http://www.aceee.org/state-policy/scorecard
Contact:
Amy Boyd, Senior Attorney
617-742-0054 x102, aboyd@acadiacenter.org
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
617-742-0054 x107, kdunlop@acadiacenter.org
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
Acadia Center Commends CT on #6 Energy Efficiency Ranking; Sees Opportunities for Higher Ranking Next Year
Connecticut ranks #6 among all states for its energy efficiency efforts, according to the 2015 State Energy Efficiency Scorecard released today by The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE), a national nonpartisan organization. Connecticut held steady at the #6 spot from last year’s ranking.
“Connecticut deserves real credit for remaining a top ten performer in the rankings,” said William E. Dornbos, Acadia Center’s Connecticut Director and Senior Attorney. “Connecticut’s strong commitment to cost-effective energy efficiency helps give the state a chance to thrive – saving consumers money on their energy bills, creating jobs in the home performance industry, and growing our economy through local investments made in nearly all of our towns and cities.”
Acadia Center reviewed the Scorecard and found that an area of particularly high scoring for Connecticut is in the “utility and public benefits programs and policies” category – the largest portion of the Scorecard’s total score. Connecticut’s utility-administered energy efficiency programs demonstrated excellent national performance, earning more points for Connecticut than forty-six other states. Only Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont scored higher in this category.
Acadia Center identified two areas in the Scorecard where Connecticut could increase its score by next year – building energy codes and combined heat and power. Specifically:
- Connecticut has not yet implemented the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC). Connecticut law requires the state to adopt the 2012 IECC within 18 months of its publication date of May 2011. Connecticut is now almost three years past that deadline. Most leading states have already adopted the 2012 IECC.
- Connecticut has not put in place sufficient programs and incentives to speed the deployment of combined heat and power (CHP), an efficient and clean way to generate electricity and produce heat through the use of a single fuel, usually natural gas. CHP projects are highly efficient because they generate electricity on-site – rather than at remote power plants – and they use the waste heat for heating or industrial needs. Connecticut was an early leader in deploying CHP, but has stalled on that front more recently.
“The gaps identified in the Scorecard should guide Connecticut’s energy policy actions,” said Dornbos. “We need to act with much more urgency in updating building energy codes, deploying CHP, and with other efficiency reforms because we’re missing out on the tremendous benefits they can offer our economy and quality of life. We can and should do more on efficiency, and we look forward to working with Connecticut policymakers to accelerate progress on cost-effective energy efficiency over the next year.”
Acadia Center is a member of Connecticut’s Energy Efficiency Board (EEB), which is a stakeholder body that has statutory responsibility for advising and assisting the state’s utilities in developing and implementing cost-effective energy efficiency plans for electricity and natural gas. The EEB recently approved a new three-year energy efficiency plan that is now before the Department of Energy and Environmental Protection for its regulatory review and approval. The plan proposes energy savings targets that, if achieved, will provide over $2.1 billion in benefits to Connecticut’s residents and businesses over the life of the plan’s investment. The demand savings will be equivalent to a 262 MW power plant.
For more on ACEEE’s Scorecard, go to: http://aceee.org/state-policy/scorecard.
Contact:
William E Dornbos, Senior Attorney
860-246-7121 x202, wdornbos@acadiacenter.org
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
617-742-0054 x107, kdunlop@acadiacenter.org
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
New Study Shows Value of Solar in New Hampshire
Acadia Center today released a study that quantifies the grid and societal benefits of solar photovoltaic systems (solar PV) in New Hampshire. Establishing the value of distributed resources is increasingly important as states explore ways to meet energy needs and deploy clean energy resources. Acadia Center has also released Value of Solar studies for Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island and Vermont , and Maine’s Public Utilities Commission completed a similar type of analysis to inform decision making processes in that state.
Acadia Center assessed the grid and societal value of six solar PV systems to better understand the overall value that solar PV provides to the grid. By evaluating an array of configurations, this analysis determines that the value of solar to the grid – and ratepayers connected to the grid – ranges from 19-24 cents/kWh, with additional societal values of 6.7 cents/kWh
“Solar generation is a valuable local energy resource that provides significant benefits to ratepayers,” said Ellen Hawes, Senior Analyst, Energy Systems & Carbon Markets. Solar PV provides unique value to the electric grid by reducing energy demand, providing power during peak periods, and avoiding generation and related emissions charges from conventional power plants. The overall grid value of solar is the sum total of these different benefits.
In addition to the value that solar provides to the grid, Acadia Center’s study finds that solar PV provides broader societal benefits, including environmental gains from reduced or avoided greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants. “Societal benefits should be included when assessing the overall costs and benefits of solar PV and determining additional incentives,” said Leslie Malone, Acadia Center Senior Analyst and an author of the report.
Currently, net metering is capped in New Hampshire, and utilities in the state are quickly reaching capped limits. A bipartisan group of legislators are looking at the possibility of temporarily raising the cap, while directing the Public Utilities Commission to revise how net-metered solar PV is credited.
“We hope that adding to the understanding of the value that solar provides to the grid and ratepayers will help inform this proceeding,” said Malone. One of the key findings of this analysis is that a “flat” system of compensation – such as net metering – can distort the market for solar PV by inadequately valuing the benefits that west-facing systems provide in mitigating costs driven by afternoon peak demand. The analysis also shows that in all cases, the value to the grid is more than the average residential retail rate of solar PV.
Acadia Center will be presenting the results of this study to the New Hampshire Energy Efficiency and Sustainable Energy (EESE) Board meeting on Friday, October 16th. For more information and methodology see:
http://acadiacenter.org/document/solarpv-nh
Contact:
Ellen Hawes, Senior Analyst, Energy Systems and Carbon Markets
802-649-1140, ehawes@acadiacenter.org
Leslie Malone, Senior Analyst
401-276-0600, lmalone@acadiacenter.org
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
617-742-0054 x107, kdunlop@acadiacenter.org
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.
RGGI Can Meet Long-Term State and Federal Targets with Program Modifications
Boston – A new report from Acadia Center explains how reforms to the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) could strengthen the program to ensure that member states meet their state and federal emissions reduction targets. RGGI’s experience to-date has demonstrated that market-based solutions can achieve significant emissions reductions while creating economic benefits, and makes the participating Northeast and Mid-Atlantic states well positioned to comply with EPA’s Clean Power Plan. However, as national leaders on climate action, eight of the nine RGGI states have established economy-wide GHG reduction goals for 2050, and meeting these goals will require the states to go above and beyond the Clean Power Plan targets. Acadia Center’s report, What’s Next for RGGI?, details how the RGGI model aligns with the framework of the final Clean Power Plan, and describes the changes that can be made in the upcoming 2016 Program Review to put the RGGI states on a path to meet their long-term targets.
Key takeaways from the report:
- EPA’s Final CPP targets have been modified to level the playing field between leading and opportunity states;
- Final CPP targets will require reforms to strengthen RGGI;
- Necessary reforms will allow states to achieve 27% of their 2050 economy-wide GHG reduction requirements through RGGI;
- Without strengthening reforms RGGI will deliver only 1% of state GHG reduction requirements;
- Reducing electric sector emissions through RGGI is the most effective means of achieving economy-wide GHG reduction requirements.
“The RGGI states have designed a model that is demonstrating how emissions reductions can be achieved at low costs to ratepayers and economic benefits,” said Daniel L. Sosland, Acadia Center President.
“RGGI states are well positioned to meet the requirements of the Clean Power Plan,” said Jordan Stutt, Policy Analyst at Acadia Center. “The upcoming 2016 Program Review offers the opportunity to strengthen the program and ensure long-term emissions reductions from the power sector.”
By undertaking the following program reforms, RGGI states will ensure continuation of the program’s environmental, consumer, and economic benefits:
- Aligning the RGGI cap trajectory with long-term state GHG reduction requirements, which can be achieved through a fixed annual decline that achieves a cumulative 90% reduction in power sector emissions by 2050; and
- Restructuring or removing the cost containment reserve (CCR) mechanism to avoid the release of additional allowances that undermine RGGI’s environmental performance.
“As creators of the nation’s first market-based program for reducing CO2 emissions from the power sector, RGGI states have a strong record of leadership,” said Peter Shattuck, Director of Acadia Center’s Clean Energy Initiative. “RGGI’s next phase can keep states on track for demonstrating the viability and benefits of sound climate policy.”
For more information on RGGI and the program’s performance to-date, see: http://acadiacenter.org/document/rggi-a-model-program-for-the-power-sector-2015-update
Contact:
Peter Shattuck, Director, Clean Energy Initiative
pshattuck@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742-0054 x103,
Jordan Stutt, Policy Analyst
jstutt@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742-0054 x105
Kiernan Dunlop, Communications Associate
kdunlop@acadiacenter.org, (617) 742- 0054 x107
###
Acadia Center is a non-profit, research and advocacy organization committed to advancing the clean energy future. Acadia Center is at the forefront of efforts to build clean, low-carbon and consumer-friendly economies. Acadia Center provides accurate and reliable information, and offers a real-world and comprehensive approach to problem solving through innovation and collaboration.